Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, has emerged as a significant public health concern globally and in India. As the World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in 2022, the awareness and measures to control its spread have intensified worldwide. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of the current situation of Mpox in India, including its symptoms, preventive measures, treatment options, and government response.
Overview and Features of Mpox
Mpox is a zoonotic viral infection, meaning it can spread from animals to humans. It is caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes the variola virus that causes smallpox. Although not as contagious or deadly as smallpox, Mpox can cause severe illness, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Mpox typically appear 5 to 21 days after exposure and can last for 2 to 4 weeks. The infection usually begins with:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Back pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Chills
- Exhaustion
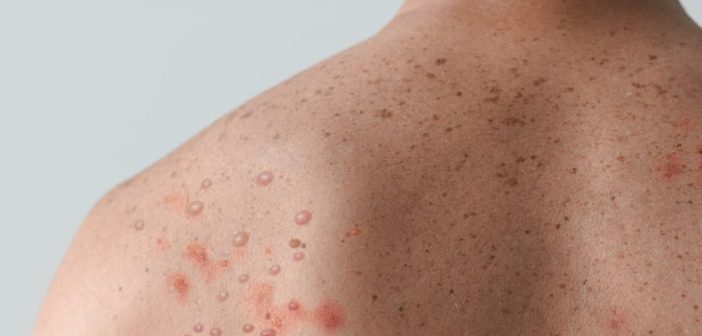
Within 1 to 3 days after the onset of fever, patients typically develop a rash, often beginning on the face before spreading to other parts of the body, including the palms and soles. The rash progresses through several stages before scabbing over and falling off.
Prevention Measures
Preventing Mpox primarily involves reducing the risk of human-to-human transmission, which occurs through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated materials. The following measures are recommended:
- Avoid Close Contact: Steer clear of contact with people who are symptomatic or have visible lesions.
- Hand Hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
- Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Healthcare workers should use PPE, including gloves and masks, when treating suspected or confirmed cases.
- Vaccination: The smallpox vaccine has shown effectiveness against Mpox. Although it is not widely available, it may be used for individuals at high risk of exposure.
Treatment Options
While there is no specific treatment for Mpox, supportive care can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Antiviral drugs developed for smallpox, like Tecovirimat, have shown efficacy against Mpox and are being used in severe cases. Additionally, the Indian government is monitoring antiviral treatments and the deployment of vaccines as part of its strategy to contain the outbreak.
Government Response and Concerns
The Indian government has been proactive in its response to the Mpox outbreak. Key measures include:
- Surveillance and Monitoring: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) have been closely monitoring the situation. Screening at airports and isolation of suspected cases are being strictly enforced.
- Advisories to States: States have been advised to set up isolation wards in hospitals and ensure that any suspected cases are immediately reported and samples are sent to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) in Pune for testing.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Efforts to educate the public about the symptoms, transmission, and prevention of Mpox have been ramped up. The Union Health Ministry has issued guidelines to educate the public and healthcare providers.
The Indian government is particularly concerned about the virus’s potential spread given the country’s large population and the risks of overburdening the healthcare system. To mitigate these risks, the government is emphasizing early detection and isolation, alongside strengthening healthcare infrastructure to manage potential outbreaks.
Current Situation in India
As of now, India has reported several cases of Mpox, with the majority being isolated incidents traced back to international travel. However, local transmission, while limited, has raised concerns about the virus gaining a foothold in the community. States like Kerala and Delhi have reported cases, prompting heightened vigilance and monitoring.
While the number of cases remains relatively low compared to other countries, the death of a 22-year-old man in Kerala in 2022 due to Mpox complications underscored the seriousness of the infection. The Indian government continues to keep a close watch, with ongoing testing and monitoring efforts (Medindia) (Wikipedia).
Global Context and India’s Role
The global response to Mpox has been robust, with WHO leading efforts to contain the virus. India, with its extensive experience in managing outbreaks of diseases like COVID-19, is playing a significant role in the global response. The country has also been part of discussions on equitable access to vaccines and treatments, given the challenges of vaccine distribution in lower-income countries.
Final Thoughts
Mpox represents a new challenge for public health systems, not just in India but globally. With its potential to cause severe illness and the risk of spreading in densely populated regions, continued vigilance and proactive measures are essential. The Indian government’s comprehensive approach, focusing on surveillance, treatment, and public awareness, is crucial in ensuring that Mpox does not become a widespread public health issue in the country.
While the situation remains under control, it is imperative for the public to stay informed and follow the recommended preventive measures. Early detection and prompt medical attention are key to managing the disease effectively. As the global situation evolves, India will need to remain adaptive and responsive to new challenges posed by Mpox.
By understanding the features, symptoms, preventive strategies, and treatment options, as well as the government’s proactive steps, the public can better protect themselves and contribute to the overall effort to control Mpox in India.