An innovative technique developed by researchers in Bengaluru has the potential to revolutionize the future of energy-efficient lighting. Scientists at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology, have devised a method to enhance the stability of perovskite nanocrystals, a crucial component in next-generation lighting technologies.
Lighting accounts for nearly 20% of global electricity consumption, with advancements over the years significantly improving energy efficiency. The transition from incandescent and fluorescent bulbs to LEDs, first developed in the 1960s and commercialized after the groundbreaking work of Shuji Nakamura in 1993, has been a major milestone. Today, OLEDs, QLEDs, and Micro/Mini-LEDs are shaping the future, each with unique advantages and limitations. OLEDs offer flexibility but have shorter lifespans, QLEDs provide precise color control but face resource scarcity, and Micro/Mini-LEDs ensure high brightness but come with steep production costs.
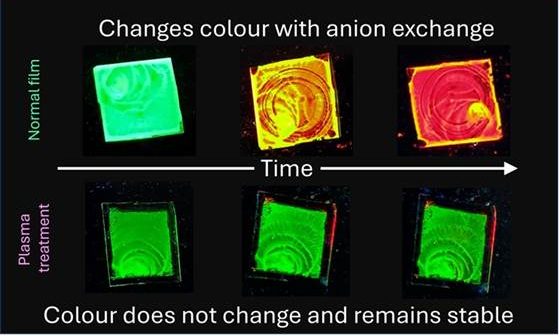
Perovskite-based LEDs (PeLEDs) combine the strengths of OLEDs and QLEDs, making them an attractive choice for advanced lighting solutions. However, their commercial viability has been hindered by sensitivity to heat and moisture and color instability caused by anion migration. The new method developed by the CeNS team, led by Pralay K. Santra, effectively addresses these challenges.
Researchers synthesized green light-emitting cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals using a hot injection method with oleylamine as a passivating ligand. To enhance stability, they employed argon-oxygen plasma treatment, which immobilizes surface ligands by creating a cross-linked, hydrophobic layer. This approach significantly reduces anion migration and improves color stability by several orders of magnitude.
This breakthrough, recently published in the journal Nanoscale, marks a major step toward durable and efficient optoelectronic devices. With further development, this innovation could pave the way for the widespread adoption of PeLEDs, redefining lighting technology for a more sustainable future.